Mocking 이란?
Controller Test를 위해선 Mocking에 대해 알고 있어야 하는데요. Mock은 테스트를 위해 실제 객체를 사용하는 것처럼 테스트를 위해 만든 모형으로 가짜 객체를 의미합니다.
Mock을 이용해서 테스트하는 과정을 Mocking이라고 부르며, 웹 애플리케이션 환경에선 Servlet Container와 Dispatcher Servlet이 메모리에 로딩되지만, Mocking을 하면 실제 테스트 컨테이너를 사용하기 때문에 Mocking을 통해 의존성을 단절시킨 상태로 테스트할 수 있습니다.
SpringBoot 환경에서 테스트 코드를 작성할 때 @SpringBootTest + @AutoConfigureMockMvc 또는 @WebMvcTest를 사용하는데요. 차이점을 가볍게 알아보고 가겠습니다.
@WebMvcTest vs @AutoConfigureMockMvc
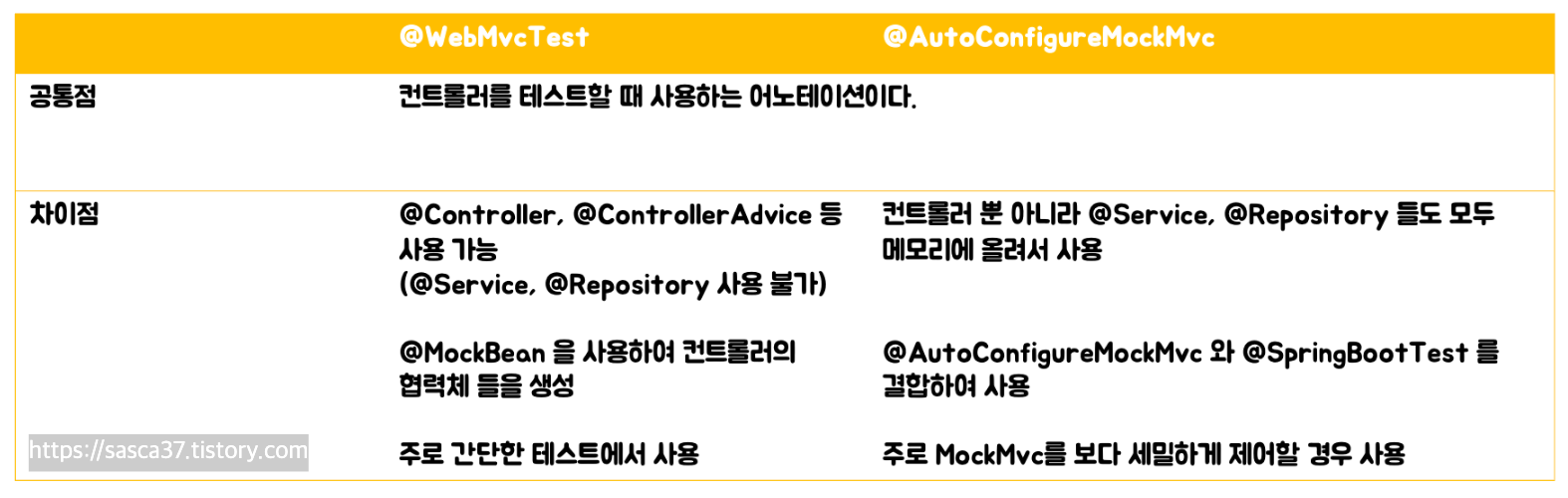
@SpringBootTest의 경우 Mock Container 또는 Servlet Container 설정 가능합니다. default는 Mock Servlet을 사용하며, classpath에 WebFlux가 있거나 servlet APIs가 없으면 Application Context를 띄웁니다.
@WebMvcTest와 @AutoConfigureMockMvc는 같이 사용할 경우 java.lang.IllegalStateException: Configuration error: found multiple declarations of @BootstrapWith for test class 오류가 발생합니다.
그 이유는 서로 Mocking을 하면서 충돌이 발생했기 때문입니다.
@WebMvcTest(PostController.class)
public class PostControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@MockBean
private PostService postService;
@MockBean
private UserService userService; // 종속성 존재로 MockBean 등록
}- @WebMvcTest의 경우 @Service, @Repository 의존성을 배제하기 때문에 테스트에서 사용되지 않더라도, 실제로 사용되고 있는 종속 서비스가 있다면 다음과 같이 @MockBean으로 등록해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 Failed to load ApplicationContext 에러를 만날 수 있습니다.
@MockBean vs @Autowired
@Autowired의 경우 실제 빈을 찾아 주입해 주는 용도로 구현된 내용을 사용하게 됩니다.
@MockBean의 경우 가짜 객체를 가져온 형태로 spring-boot-test의 Mockito와 결합하여 실제 로그인한 사용자 또는 인가되지 않은 사용자 등의 테스트가 가능합니다. @MockBean과 Mockito를 사용하여 @WithMockUser, @WithAnonymousUser, @WithUserDetails 등 사용자 관련 인증을 처리할 수 있습니다.
@WithMockUser 등 Security에서 사용되는 어노테이션은 포스팅을 참고 부탁드립니다.
Controller Test 예제
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.security.test.context.support.WithAnonymousUser;
import org.springframework.security.test.context.support.WithMockUser;
import org.springframework.security.test.context.support.WithUserDetails;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.mockito.ArgumentMatchers.any;
import static org.mockito.ArgumentMatchers.eq;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.doThrow;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers.print;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class PostControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@MockBean
private PostService postService;
@Test
@WithMockUser
void 포스트수정() throws Exception{
String title = "title";
String body = "body";
// mocking
when(postService.modify(eq(title), eq(body), any(), any()))
.thenReturn(Post.fromEntity(PostEntityFixture.get("userName", 1, 1)));
mockMvc.perform(put("/api/v1/posts/1")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsBytes(new PostModifyRequest(title, body)))
).andDo(print())
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}
}- @SpringBootTest와 @AutoConfigureMockMvc의 경우 @Service, @Repository 모두 메모리에 올리기 때문에 관련된 종속 빈 들의 정보를 가져올 수 있어서 추가 @MockBean이 필요하지 않습니다.
- org.mockito 라이브러리를 통해 로그인하지 않은 사용자, 로그인 한 사용자가 포스트 작성 등의 상황을 가정해서 테스트할 수 있습니다.

